VPN (Virtual Private Network)
What is a VPN?
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a service that enhances your online privacy and security by masking your IP address and encrypting your data.
How does a VPN work?
When you use a VPN for browsing, it encrypts your data, and creates a secure tunnel between your device and its VPN server to reroute your internet traffic. In this way, your Internet Service Provider (ISP) can only detect your connection to this VPN server and is unable to monitor your actual online activities. Similarly, the websites you visit can only see the requests from the VPN server, and detect the server’s IP address instead of yours. Consequently, your IP address is concealed, and your online activities remains hidden, and your browsing becomes more private and secure.
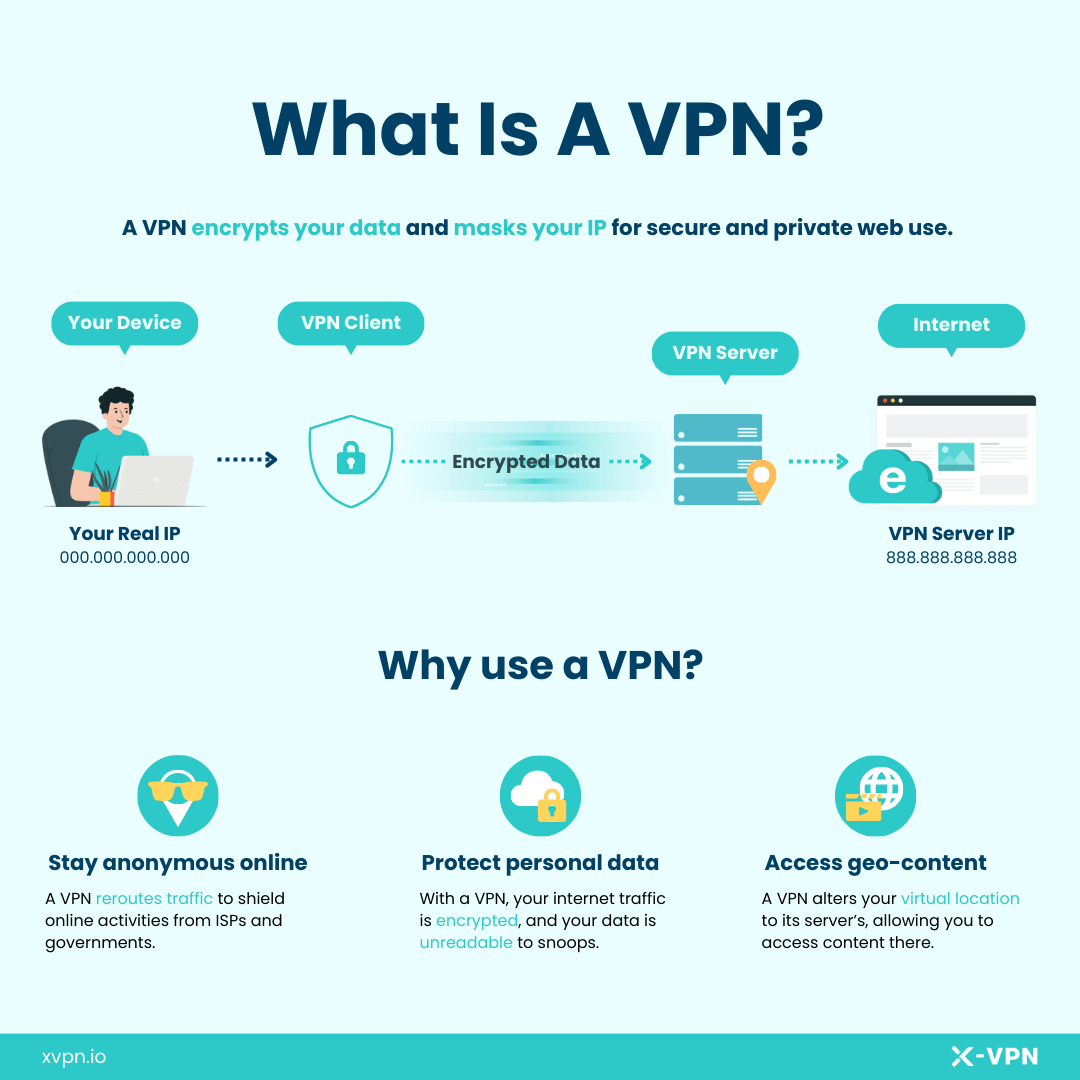
The primary roles of VPNs include:
1. Privacy - By masking your IP address and location, a VPN ensures your browsing activity is private and not tracked.
2. Security - A VPN protects your data with end-to-end encryption, safeguarding your information from hackers, especially on public Wi-Fi networks.
3. Access - A VPN alters your virtual location to its server’s, allowing you to access content there.
FAQ
1. What is a VPN connection?
A VPN connection is a secure and encrypted channel that a VPN creates between your device and its VPN server. Your data will be transmitted encrypted through this channel, making it more secure as it is less likely to be accessed and cracked. Also, since your data has been transmitted to the VPN server through this encrypted channel, the VPN server will forward your traffic so that third-party websites will not be able to trace your real IP address.
2. What is a VPN used for?
A VPN is usually used to enhance online privacy, secure data on public Wi-Fi, access region-blocked content, and prevent tracking. It's essential for safe browsing and maintaining digital anonymity.