IPv6
What is IPv6?
IPv6, or Internet Protocol version 6, is the latest version of the Internet Protocol used to identify and locate computers on networks and direct internet traffic.
IPv6 employs 128-bit addresses, formatted as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons—for instance, "2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334." With this system, we can uniquely address approximately 3.4 × 10^38 devices—enough for every grain of sand on Earth to have its own IP address.
Advantages of IPv6
1. Wider address space
With Internet users and devices surging, IPv4's 4.3 billion IP addresses fall short. IPv6 offers vastly more unique combinations to meet future IP address demands.
2. Simplified format
IPv6 features a simplified header structure that facilitates faster data processing compared to the more complex headers in IPv4.
3. No Network Address Translation
With enough unique public IP addresses for each device, there's no need for Network Address Translation(NAT)—a boon for streamlined connectivity.
4. Enhanced Security
IPv6 inherently supports the IPSec protocol, making data transmission more secure.
Challenges of IPv6
1. Compatibility Issues
IPv4 and IPv6 computers cannot communicate directly with each other, and many existing systems and facilities built on IPv4 do not directly support or recognize IPv6.
2. Transition Costs
Shifting from IPv4 to IPv6 could entail significant expenses due to necessary hardware replacements, software updates, and training personnel.
3. Security Concerns
IPv4 is still widely used, and many ISPs and service providers have not yet provided IPv6 services or updated their security infrastructure to adapt to IPv6. For example, some VPN service providers only provide technical services for IPv4, and are unable to encrypt IPv6 traffic, which results in IPv6 leak even when VPNs are used.
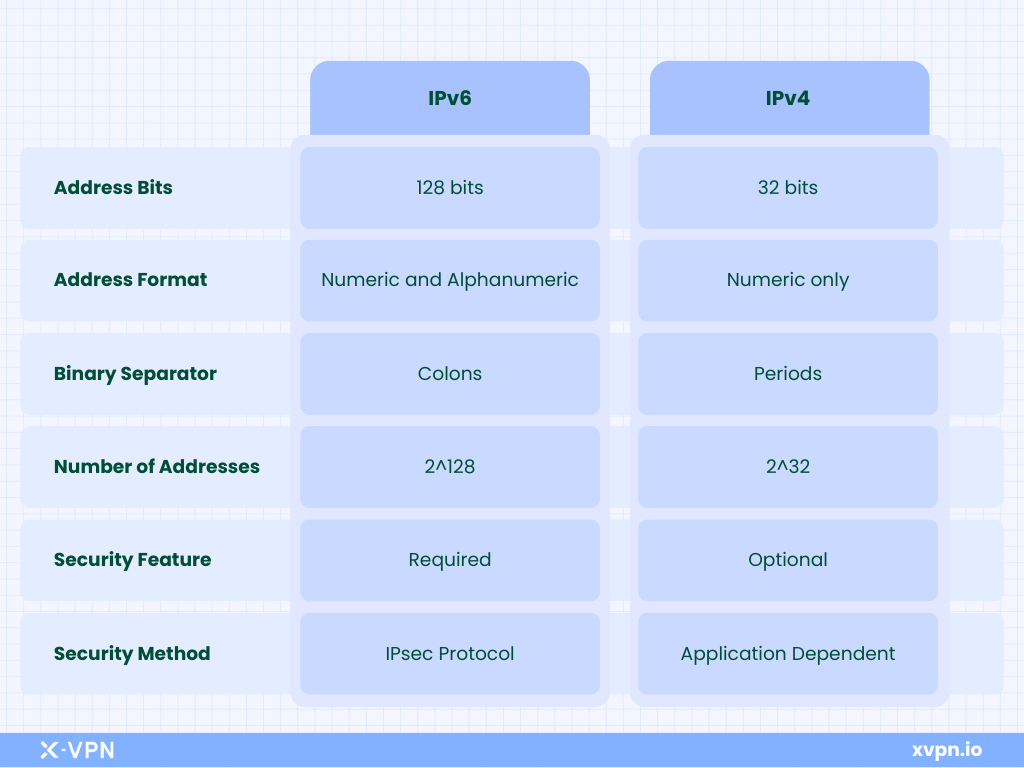
IPv6 vs. IPv4
FAQ
1. Can I enable an IPv6 address on my device?
Most operating systems (including Windows, macOS, and Linux) support IPv6 by default; you can toggle this feature in your device's network settings.
2. How do I know if my connection uses an IPv6 address?
To check your connection's IPv6 status, utilize tools like X-VPN's "IP address checker" for immediate verification.
3. How can I prevent IPv6 leaks?
To stop IPv6 leaks, use a VPN with automatic IPv6 leak protection like X-VPN. After connecting to the VPN, run an IPv6 leak test to make sure that your VPN works.
