Have you ever checked your IP online and seen something like 123.198.03.221? Smart! That’s your public IP address, which is assigned by your internet service provider to communicate with the public internet. But what about a private IP address? It stays within your local network, helping devices like your computer and printer talk to each other.
Now, you might wonder: ‘Do I really have both a public and private IP? How to tell if an IP address is public or private? And how do I find them?’ Don’t worry, I’ve got you covered—let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a Public IP Address?
Does your house have both a room number and a home address? A public IP address, like the home address number, is a unique identifier assigned by your internet service provider (ISP).
Just like your home address helps strangers find you, your public IP helps the internet send data to and from your device, whether you’re browsing, emailing, or streaming.
Additionally, each device needs a unique public IP. This ensures your online requests—like visiting websites or downloading files—get to the right place without any issues.
Static IP vs Dynamic IP
Public IPs come in two types: static and dynamic.
Static IP: A static IP stays the same all the time, like the IP address for google.com. Normally, websites and services use static IPs so they’re easy for visitors to find.
Quick fact: You might be thinking, “But I never see an IP address when I browse google.com!” That’s because DNS (Domain Name System) translates domain names like “google.com” into IP addresses behind the scenes. This way, you don’t have to remember long numbers—just easy-to-remember names. Pretty cool, right?
Dynamic IP: A dynamic IP changes whenever you reconnect the internet. They are usually used by personal devices, because ISPs manage them by randomly assigning new addresses each time you reconnect.
Can we track public IP addresses?
Yes, because your ISP assigns and manages your public IP, so they can easily track your general location and browsing activities. Additionally, websites you visit can also see your IP address and track your location and actions on this site.
But don’t worry—using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) can mask your real IP address.
What is a Private IP Address?
Now, how about your private IP address? It’s like your room number. Only people in your house can see it. Similarly, your private IP address is used within your home, business, or school network—a private environment—and isn’t visible to the global internet.
💡For example, if you want to print a file from your computer, the computer needs to share it with the printer, and the private IP is the key to making sure they find each other.
Unlike your public IP, your private IP is assigned by your router, giving each device in your home a unique ‘name’ within the network. So they can be reused across different local networks.
Can we track private IP addresses?
Yes, but since private IPs are visible within your “home” network, only devices connected to the same local network can trace you.
How Public and Private IPs Work Together
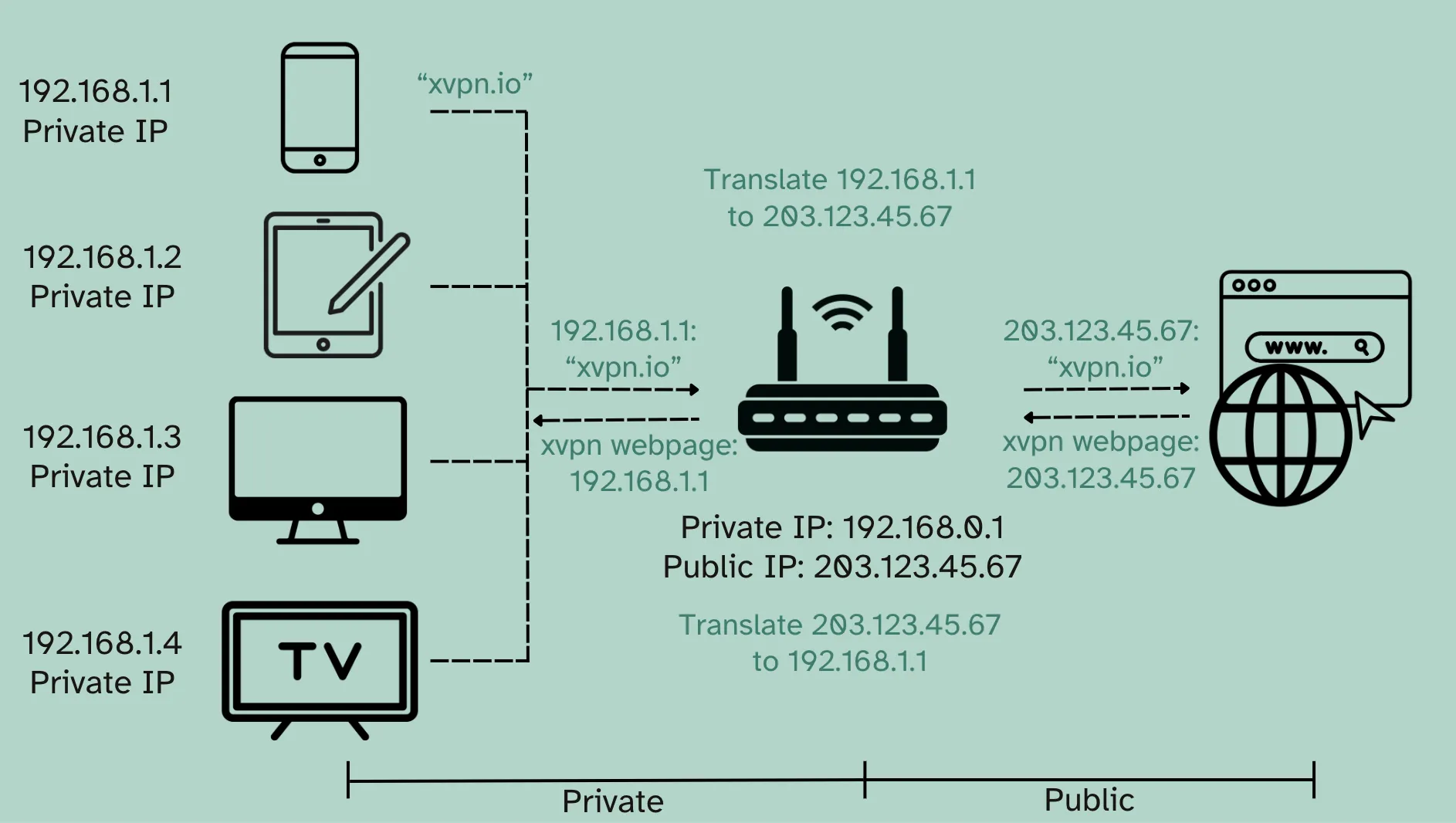
Let’s start with an example to help you understand how public and private IP addresses work together.
Now, given that you’re at home and want to use your phone to browse X-VPN’s official website.
You have four devices (phone, iPad, PC, and TV) all connected to your home router. Each device has its own private IP address, which allows them to communicate with each other and lets your router identify them within your home network.
OK then, let’s see what happens when you type in “xvpn.io” on your phone:
- Your phone sends the request to your router.
- The router receives the message: “Phone wants to visit xvpn.io.”
- The target website can’t see your phone’s private IP address, so, your router uses Network Address Translation (NAT) to translate your phone’s private IP into your home’s public IP address (assigned by your ISP).
- The X-VPN website sees your public IP address and sends the webpage data back to your router.
- Once the data reaches your router, NAT reverses the public IP back into your phone’s private IP and sends the info to the correct device—your Phone, not your PC!
In short, your private IP is used for communication within your home, while your public IP is used for communication with the internet. NAT acts as a middleman, translating between the two to make sure your requests reach the internet, and the responses come back to the right device.
📺 You can dive deeper into What Is NAT by watching this insightful video:
Difference Between Public and Private IP
So, what’s the difference between public and private IP? I believe you may have some answers but let’s recover it again!
Scope
Public IP: The scope of public IP is global, meaning it can be used and accessed anywhere across the internet.
Private IP: The scope of private IP is local, meaning it will be limited to only your home, office or school’s internal network.
Function
Public IP: The main responsibility of public IP is to communicate outside your private network, to connect your private network to the internet.
Private IP: The key function of private IP is to communicate within your private network, helping devices inside the network talk to each other.
Visibility
Public IP: A public IP address will be visible to everyone on the internet, including ISPs, websites and services you interact with.
Private IP: A private IP address will be hidden and only visible to devices within the same private network.
Uniqueness
Public IP: Every public IP should be unique and never reused across the internet.
Private IP: Each private IP just needs to be unique within the local network and can be reused.
Assignment
Public IP: ISPs assign and manage public IPs.
Private IP: Router is responsible for assigning private IPs to each device connected to.
Cost
Public IP: Having a public IP address always comes with additional costs, especially when you need a static IP or multiple public IPs.
Private IP: Private IP addresses are free. They don’t require any extra cost since they are managed by your router.
Range
Public IP Ranges: Due to keeping unique across the global internet, public IP addresses encompass the entire global IP address pool, including all IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. That is, they can contain every number.
Private IP Ranges: Unsurprisingly, private IP addresses will be limited to specific ranges reserved by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). They have to obey the following ranges:
- Class A: 10.0.0.0 — 10.255.255.255
- Class B: 172.16.0.0 — 172.31.255.255
- Class C: 192.168.0.0 — 192.168.255.255
| Category | Public IP | Private IP |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Global | Local |
| Function | Communicates outside the private network | Communicates within the local network |
| Visibility | Visible to everyone on the internet | Hidden, visible only to devices in the same network |
| Uniqueness | Unique across the entire internet | Unique within the local network, can be reused |
| Assignment | Assigned by ISPs | Assigned by routers |
| Cost | May incur costs | Free |
| Range | Uses all available IPv4 and IPv6 addresses | Restricted to specific ranges reserved by IANA |
How to Find Your Private IP Address
Finding your private IP address is easy, and it’s helpful when troubleshooting network issues between devices. Here’s how you can do it depending on your device:
For Windows:
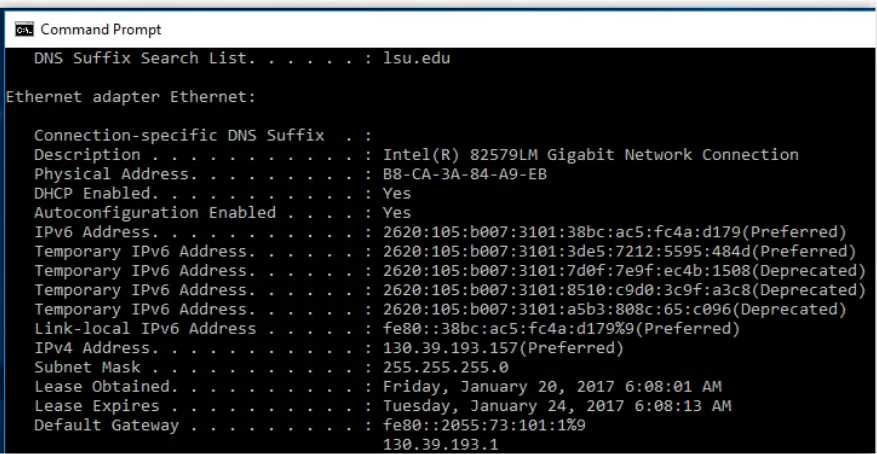
- Click the Windows icon and type “Command Prompt” in the search bar. Open the Command Prompt.
- Type
ipconfigand press Enter, waiting for the answers followed. - Look for the line that says IPv4 Address. The number like
192.168.x.xor10.x.x.xis your private IP address.
For macOS:
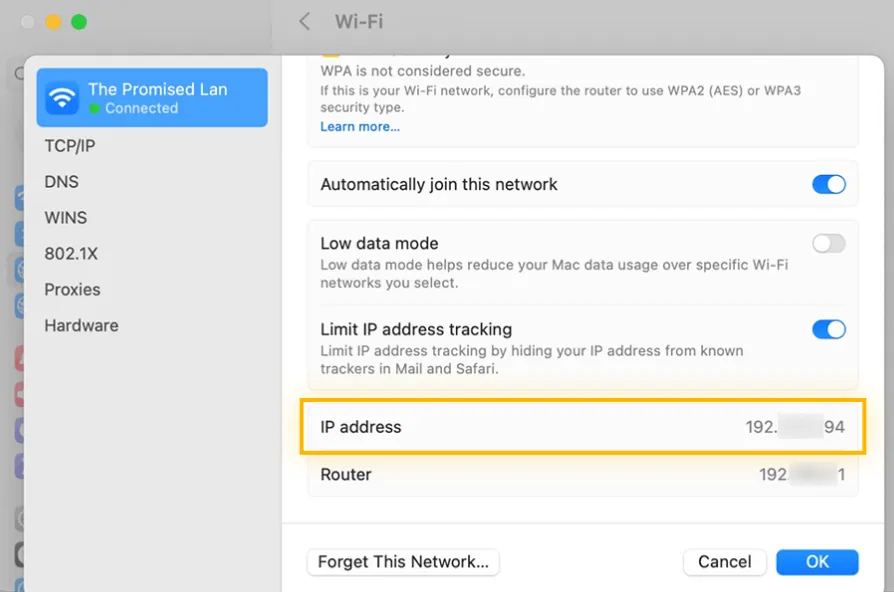
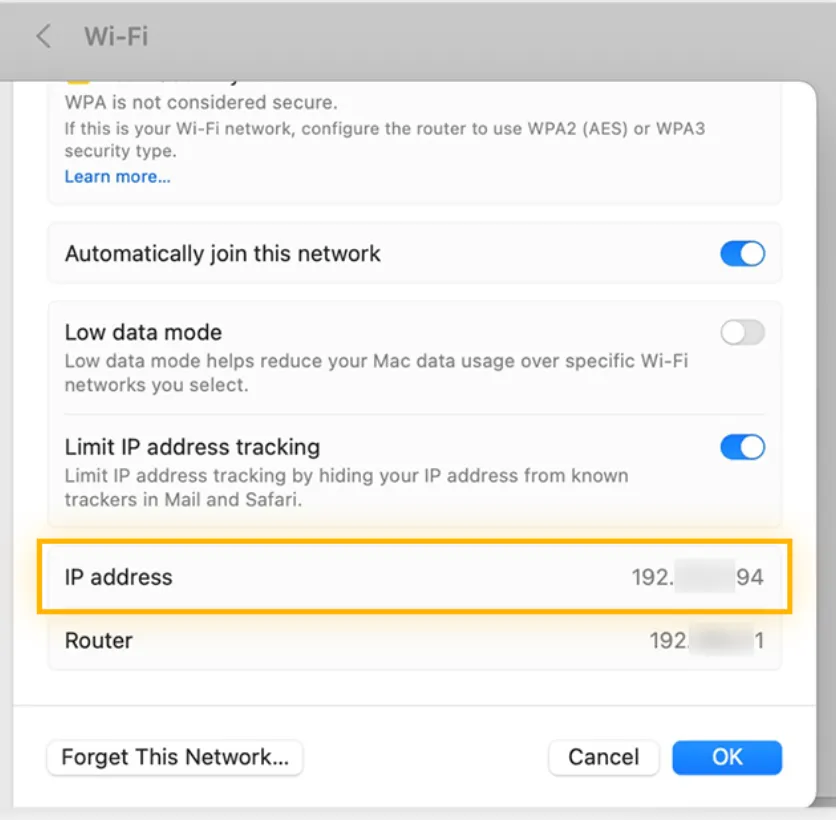
- Click the Apple icon in the top-left corner and select System Settings.
- Go to Network and select your active network connection (Wi-Fi or Ethernet).
- In the network settings, you’ll see the IP Address listed, which is your private IP (usually something like
192.168.x.x).
For Android:
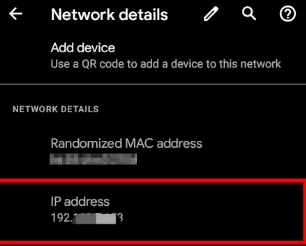
- Open Settings and tap on Wi-Fi.
- Find your connected Wi-Fi network and tap on it.
- In the details, look for IP Address—this is your private IP address.
For iPhone/iPad:
- Open the Settings app and tap on Wi-Fi.
- Tap on the information icon (ℹ️) next to your connected Wi-Fi network.
- Your private IP address will be listed under IP Address.
For a Router’s Admin Page
If you want to see the private IP addresses of all devices connected to your network:
- Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address (usually
192.168.1.1or192.168.0.1). - Log in with your router credentials.
- Navigate to the connected devices or network section, where you’ll see the private IP addresses of all devices connected to your router.
How to Find Your Public IP Address
The easiest way to check your public IP address is to search “What is my IP address?” in your browser, and your public IP will appear at the top of the results.
Alternatively, you can use our IP checker tool on the X-VPN official website.
📺 To learn more about IP addresses, don’t miss the video below:
Conclusion
Every device connected to your router has its own private IP for internal communication, while your network has a public IP for connecting to the internet. Your private IPs are hidden and only used within your local network, but your public IP is visible to the outside world, which could expose your location or browsing activities.
But don’t worry—X-VPN can help protect your public IP without any effort! Click the button below to get protected now, with no fees or registration required!

FAQs
What is my public IP?
Your public IP address is the unique identifier assigned to your home network by your ISP. This IP is visible when you access the internet and is used to identify your network to external websites and services.
How to find public IP address?
Finding your public IP address is easy. Here are a few methods:
1. Search Engine: Simply go to a search engine (like Google) and type “What is my IP?”. Your public IP will be displayed at the top of the search results.
2. Router Settings: You can log into your router’s admin page (usually by typing 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1 in a browser) and find the public IP listed under the WAN or Internet Connection section.
What is my private IP?
Your private IP address is the address assigned to your device within your home or office network. Each device connected to your router gets a unique private IP, which allows them to communicate with other devices locally.
How to find private IP address?
You can easily find your private IP address by following these steps:
– On Windows:
1. Open the Command Prompt by typing “cmd” in the Start menu.
2. Type ipconfig and press Enter.
3. Look for IPv4 Address—this is your private IP.
– On macOS:
1. Open System Settings and go to Network.
2. Select your active network connection (Wi-Fi or Ethernet).
3. Your private IP will be listed under IP Address.
– On iPhone/Android:
1. Go to Settings and select Wi-Fi.
2. Tap on your connected network and look for the IP Address—this is your private IP.
How to check if IP is public or private?
You can tell whether an IP address is public or private based on the IP address range:
– Private IP ranges (for IPv4):
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
Any IP address within these ranges is a private IP. If the IP falls outside these ranges, it’s a public IP.
Quick Check: If your IP starts with numbers like 192.168.x.x or 10.x.x.x, it’s a private IP. Anything outside those ranges is public.





