If you’ve ever turned on a VPN and felt like your internet suddenly slowed, you’re not imagining things. A VPN can affect internet speed. Sometimes it’s barely noticeable, but a bad connection can make load times unbearably slow. The real question isn’t whether a VPN slows your connection, but why it happens and when it’s worth the effort.
Once you understand what’s going on behind the scenes, you can better balance when the trade-offs make sense, and when they don’t. Let’s break down what actually affects VPN speed and what you can do about it.
Table of Contents
What Changes When You Turn on a VPN?
Normally, your device connects directly to websites and services through your internet service provider (ISP). When you use a VPN, your traffic is encrypted and routed through a secure server before reaching its destination.
That extra step is what protects your privacy, but it also changes how your data travels. Understanding how a VPN tunnel works helps explain why speed can sometimes be affected.
Your data isn’t just traveling farther; it’s also being wrapped in encryption and unpacked again at the other end. That added protection is often crucial, making a tiny delay time well spent. Most of the time, your device barely notices the extra work.
What can matter more is that VPN traffic carries a little extra data around each packet. On some networks, this can reduce efficiency and increase retransmissions, especially if the connection is already unstable. You’ll feel that as stutter, not a constant slow crawl.
Encryption Isn’t Usually the Real Slowdown
Encryption is often blamed for VPN speed issues, but on modern devices, it’s rarely the main culprit. Today’s VPNs use highly optimized encryption that most phones and computers handle easily.
For most users, encryption adds only a tiny amount of overhead, especially when using modern protocols. Older devices can struggle more, which is why protocol choice matters. In an ongoing data stream, the fastest encryption takes microseconds.
It also helps to separate two ideas: throughput (how much data you can move) and responsiveness (how quickly the connection reacts). You can have plenty of bandwidth and still feel “slow” if latency spikes, pages stall, or video calls jitter.
Distance to the VPN Server Matters More Than Encryption
One of the biggest factors affecting VPN speed is physical distance. If you connect to a nearby server, the detour is short. If you connect to a server on another continent, your data travels much farther.
Longer distances increase latency, which can feel like slow page loads, laggy browsing, or delayed video calls. That delay can be small per request, but it adds up when a page loads dozens of elements, or when your apps constantly sync in the background.
This is why large server networks matter. With access to a broad global VPN server network, it’s easier to stay close to your real location while still protecting your privacy.
Look for a service with several thousand worldwide servers to ensure you can pick a nearby connection when you travel. A local server is usually best for speed, but a well-connected server can matter too, especially for streaming and video calls.
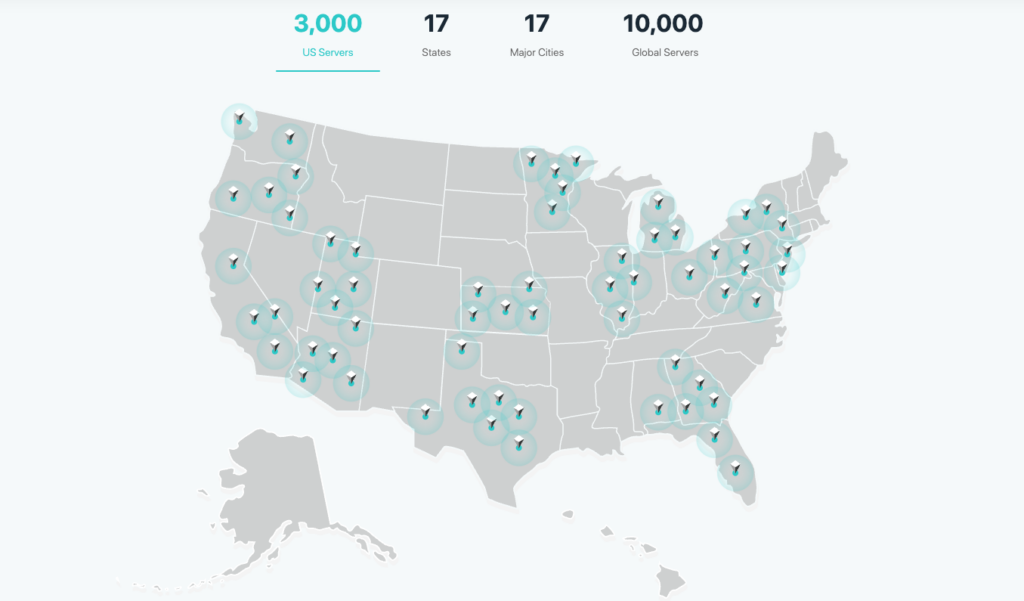
The Server Network of X-VPN
Server Congestion Can Slow Things Down
VPN servers are shared resources. If too many users connect to the same server at the same time, performance can dip.
This happens most often with:
Switching servers is often the fastest fix. A sudden slowdown doesn’t necessarily mean the VPN is bad. It’s just that a particular server is busy.
However, you shouldn’t have to spend too much time searching for a good connection. A good VPN service, like X-VPN, guides you to a fast, secure server without requiring multiple retries. The VPN either recommends a fast location or balances users automatically.

Server Congestion Akin to Traffic Jams
Sometimes Your ISP Is the Problem
In some cases, a VPN doesn’t slow your internet at all. It just exposes problems caused by your internet service provider (ISP). Many ISPs throttle streaming, gaming, or large downloads. Limiting high-bandwidth services is less expensive than expanding network infrastructure.
When you use a VPN, your ISP can’t see what kind of traffic you’re sending. This is why some people experience faster speeds with a VPN enabled, especially for streaming or downloads.
If you’ve ever wondered whether you really need a VPN, this is one of the less obvious reasons.
Routing can play a role, too. ISPs don’t always pick the most efficient path to every destination. A VPN changes the route your traffic takes, and sometimes that new route is simply cleaner and more stable. It’s not guaranteed, but it explains why “VPN on” can occasionally feel smoother than “VPN off.”
VPN Protocols Can Make a Big Difference
Not all VPN protocols behave the same way. Some focus on speed, others on compatibility or stealth. There are good reasons for all three types.
Modern protocols are designed to minimize latency and reconnect quickly on unstable networks. Choosing the right protocol can significantly improve performance, especially on mobile data or public Wi-Fi.
For example, X-VPN’s Everest protocol is designed to balance strong encryption with speed and obfuscation, reducing overhead even on unstable or restricted networks. When performance is most important, WireGuard is usually the best choice. For router compatibility, OpenVPN is hard to beat.
If your VPN feels fast at home but slow on public Wi-Fi, the protocol may be the difference. Some handle packet loss and roaming better than others, which affects how stable the tunnel feels when the network is messy.
Local Wi-Fi Still Matters
A VPN can’t fix weak Wi-Fi. If you’re in a crowded cafe network or a hotel with outdated routers, your VPN can’t improve that first leg of the connection.
Poor Wi-Fi will feel slow with or without a VPN, and encrypted traffic can make instability more noticeable. Packet loss and interference can look like “VPN slowness,” even though the bottleneck is the local network.
This is why features like a VPN kill switch matter. If the connection drops, traffic is blocked instead of leaking onto an unsecured network.
Why Free VPNs Are Usually Slow?
Many complaints about VPN speed trace back to free services.
Free VPNs often limit bandwidth, overload servers, restrict server locations, or rely on older infrastructure, which means a slow VPN experience is usually a service quality issue, not a VPN limitation.
However, not all free VPNs have the above issues. For example, X-VPN offers over 1,000 free servers to all users and provides manual selection across 26 locations. With no speed limits and no login required, you can enjoy secure browsing with X-VPN indefinitely.
Of course, free plans typically include only basic VPN functionality. If you seek more server location options and stronger, more stable VPN performance, upgrading to a paid plan is always the better choice.
Does a VPN Slow Down Streaming?
Yes, it does. Streaming is one of the most noticeable use cases for speed changes. A good VPN should handle HD and 4K streaming without buffering when connected to nearby servers.
VPNs built with streaming in mind focus on capacity and routing. For example, X-VPN’s streaming performance features are designed to reduce buffering and maintain consistent video quality.
If you’re accessing content from another country, some slowdown is normal due to distance. If buffering gets severe, try a closer server, try a different server in the same country, and then try a different protocol. In many cases, that’s enough to restore smooth playback.

What About Gaming?
Gaming is sensitive to latency. Even small delays can matter.
A VPN can help in specific cases, such as avoiding ISP throttling or stabilizing routing, but it won’t magically improve every game. Using a VPN for gaming only makes sense in certain network conditions or when you need to access global gaming resources.
If you’re competitive, measure it. Compare ping and stability with and without the VPN, and focus on consistency. A stable connection with slightly higher ping can feel better than a lower ping that spikes constantly.
Mobile Networks and VPN Speed
On mobile data, VPN performance depends heavily on signal strength and network switching. Phones frequently move between Wi-Fi, LTE, and 5G, requiring the VPN tunnel to reconnect.
Modern protocols handle this well, but brief slowdowns can occur. Always-on VPN modes improve security but can expose weak signals, making stalls more obvious when coverage is inconsistent. If disconnects happen frequently, check whether your phone’s battery saving mode is restricting background network activity for the VPN app.
How to Get the Fastest Speeds with a VPN?
A few practical steps make a big difference:
If you’re using a good VPN, most slowdowns are temporary and easy to fix.
If you want a quick sanity check, run a baseline speed test without the VPN, then repeat it with a nearby server. If ping jumps a lot, distance or routing is likely the issue. If download speed collapses only on one server, congestion is the more likely culprit.
When Slower Speeds Are Worth It?
A VPN isn’t just about speed. It’s about control, privacy, and consistency.
Using a VPN means your ISP can’t track or throttle you, public Wi-Fi becomes safer, and your IP address stays hidden. For most users, the privacy benefits outweigh a small speed reduction, especially with a well-optimized service. Strong encryption also plays a role in protecting yourself from hackers on public and shared networks.
For many people, that trade is practical, not theoretical. You’re not buying secrecy for secrecy’s sake, you’re buying a safer default on whatever network you happen to be on.
Final Thoughts
So, does a VPN slow down the internet? Sometimes, but not in the way most people think.
Modern VPNs add minimal overhead, and in some cases, they improve performance by avoiding throttling or inefficient routing. Server distance, congestion, and protocol choice matter far more than encryption itself.
X-VPN is designed to protect your data without becoming a bottleneck. With the right setup, speed and privacy don’t have to be trade-offs. Pick a nearby server from 10,000+ options, switch if it’s congested, and choose a protocol that fits your network. Done right, the VPN becomes a quiet privacy layer, not a daily annoyance.
FAQs
Does a VPN always reduce internet speed?
No. A VPN can sometimes improve speed by avoiding ISP throttling or poor routing.
Why is one VPN server faster than another?
Distance, congestion, and routing efficiency vary by server. Switching servers often fixes speed issues.
Is a paid VPN faster than a free VPN?
Almost always. Paid VPNs invest in infrastructure, while free VPNs typically limit performance. That said, some top VPNs offer free tiers with minimal limitations. X-VPN’s free version is uncapped. If you try the free version and find you need access to more speed, a low-cost subscription unlocks 10,000 high-speed premium servers.