VPN Encryption is the core of VPN functioning, safeguarding your network data against theft, snooping, or interception by hackers.
To get a clear understanding of VPN encryption, including its benefits and how it works, keep reading. We will offer a comprehensive guide that breaks down the complexities into easy-to-understand language.
Table of Contents
What Is VPN Encryption?
VPN encryption typically employs the TLS protocol and specific cryptographic algorithms to “translate” data packets into a seemingly random string of ciphertext. To outsiders, it appears as gibberish, utterly meaningless. Only those possessing the correct decryption key can restore the original content, rendering any unauthorized snooping futile—thus ensuring your private data remains securely protected.
Here’s a scenario for you to understand the term Encryption clearly.
- Scenario: Anna sends a message to Juli with a VPN.
- The Original Text: Hi, Juli!
- The Encrypted Text: gijo390jdksjfkn
- Message Read by Other One: gijo390jdksjfkn
- Message Read by Juli(who has the key): Hi, Juli!
💡In specific practical cases:
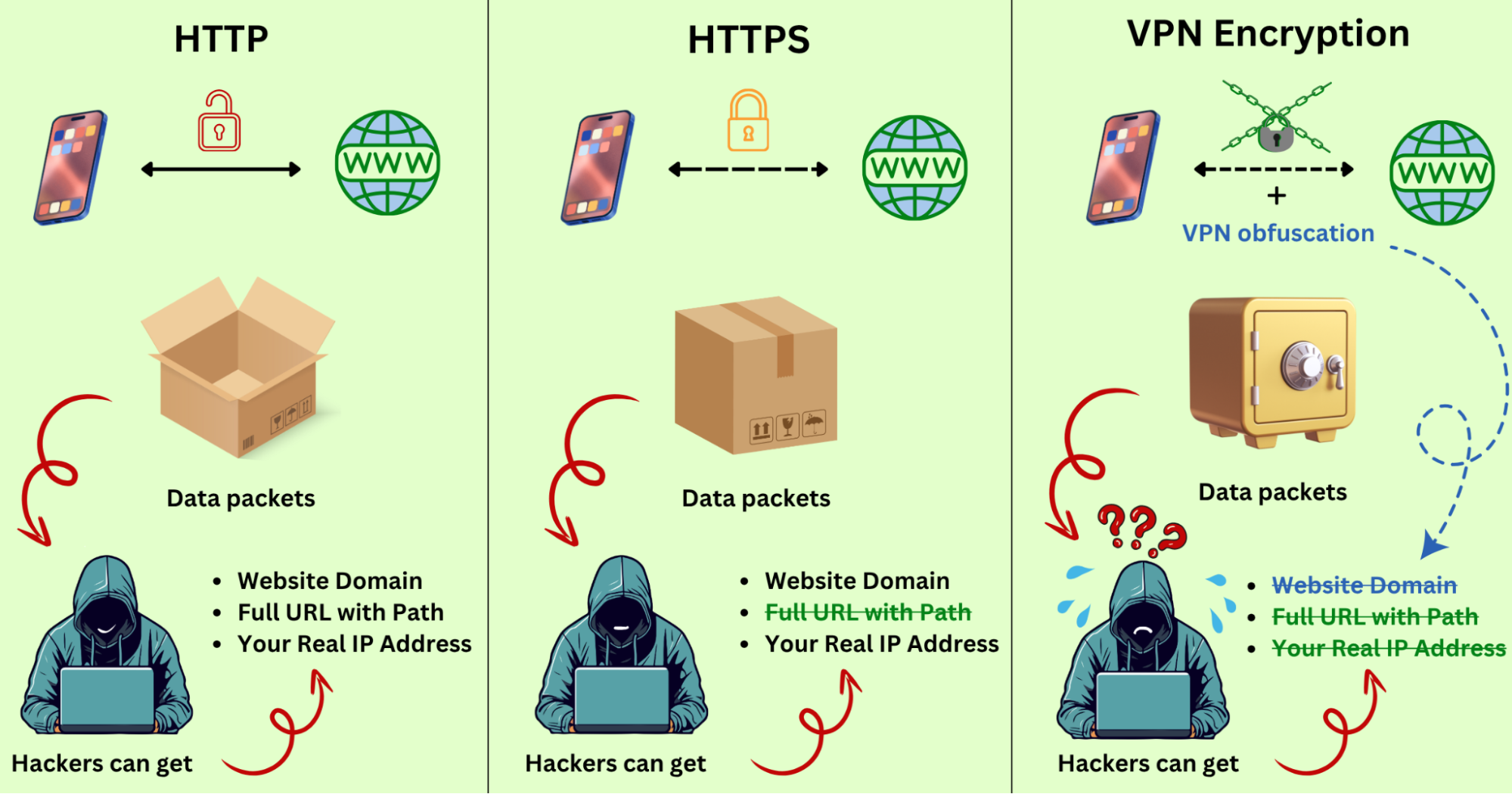
・When Accessing Unencrypted Services: When you visit applications or websites that do not support data encryption (such as pages still using the HTTP protocol), VPN encryption acts as your “invisibility cloak.” It hides your domain name, visited pages, and real IP address, preventing third parties from snooping or intercepting your data, making your online activities more private.
・When Accessing Encrypted Services: For websites already using secure protocols like HTTPS, VPN encryption adds an extra layer of protection. Beyond application-layer encryption, it wraps data packets in additional TLS protection, achieving “double encryption.” This not only makes data more difficult to decrypt but also further conceals your identity, making your digital footprint harder to track.
・Pro Tip: Some top-tier VPN services (like X-VPN) incorporate obfuscation technology alongside encryption. This “stealth capability” makes encrypted data appear as ordinary traffic, preventing detection and effectively bypassing internet censorship for a safer, freer browsing experience.
In essence, VPN encryption is the very soul of a VPN. It serves not only as the first line of defense for your privacy but also as the key to maintaining anonymity in the digital realm. Put simply, a VPN without encryption is like a safe without a lock—a hollow shell.
How Does VPN Encryption Work?
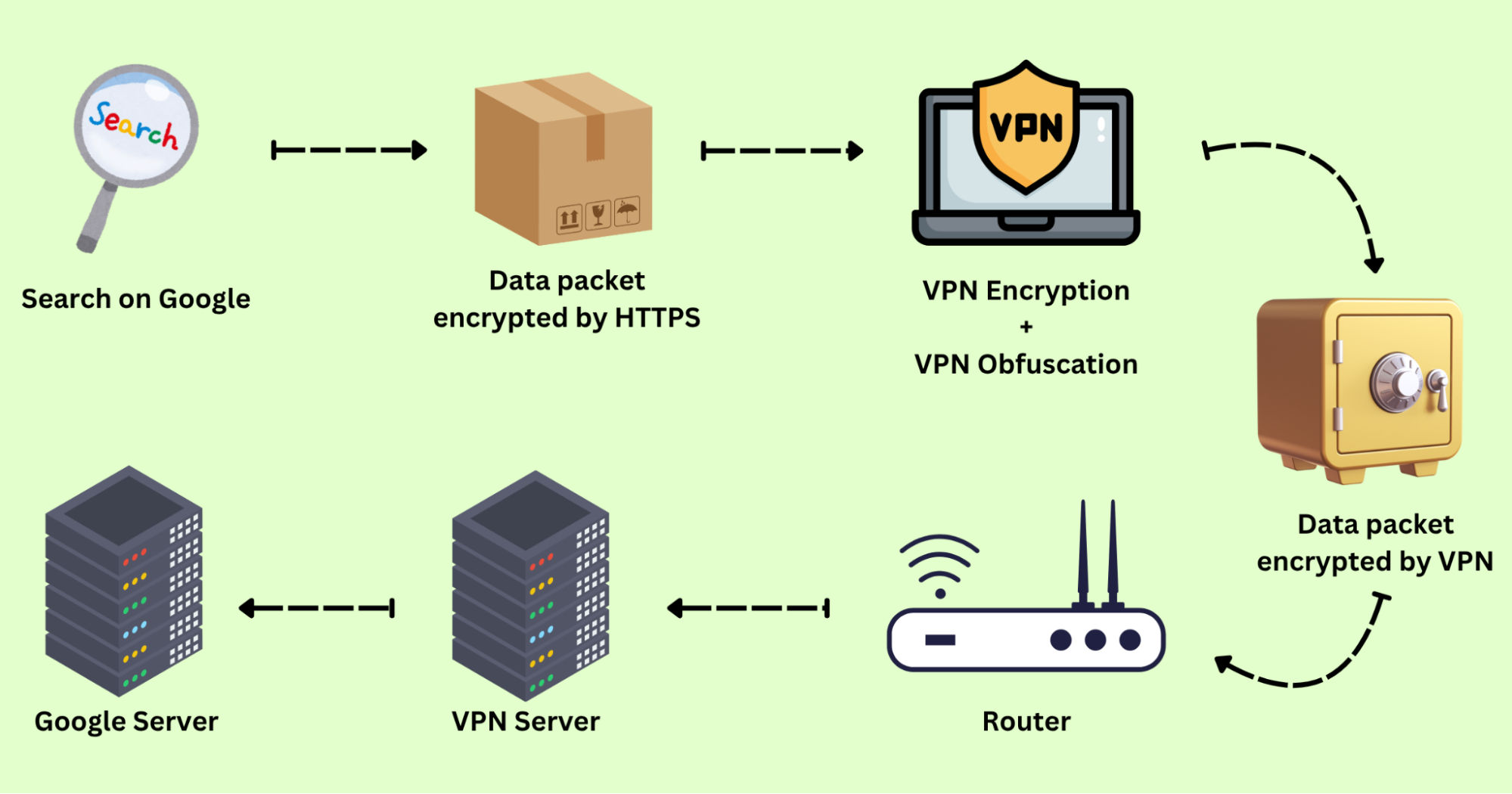
When you already have a VPN service and are ready to connect to a server to access a website, the VPN encryption mechanism will quietly activate and proceed as follows:
Step 1. Send Request
When you connect to a VPN server and begin accessing websites or applications, your request is not sent directly to the internet. Instead, they are first routed to the VPN client.
Step 2. Build a Tunnel
Upon receiving your request, the VPN client immediately establishes a “dedicated channel” for you—that is, a secure VPN tunnel. This tunnel connects the network path between you and the VPN server, effectively preventing external snooping or data tampering.
Step 3. Encrypt Data
Your online data is transmitted to the VPN server via the VPN tunnel and encrypted. Check the brief overview of the process:
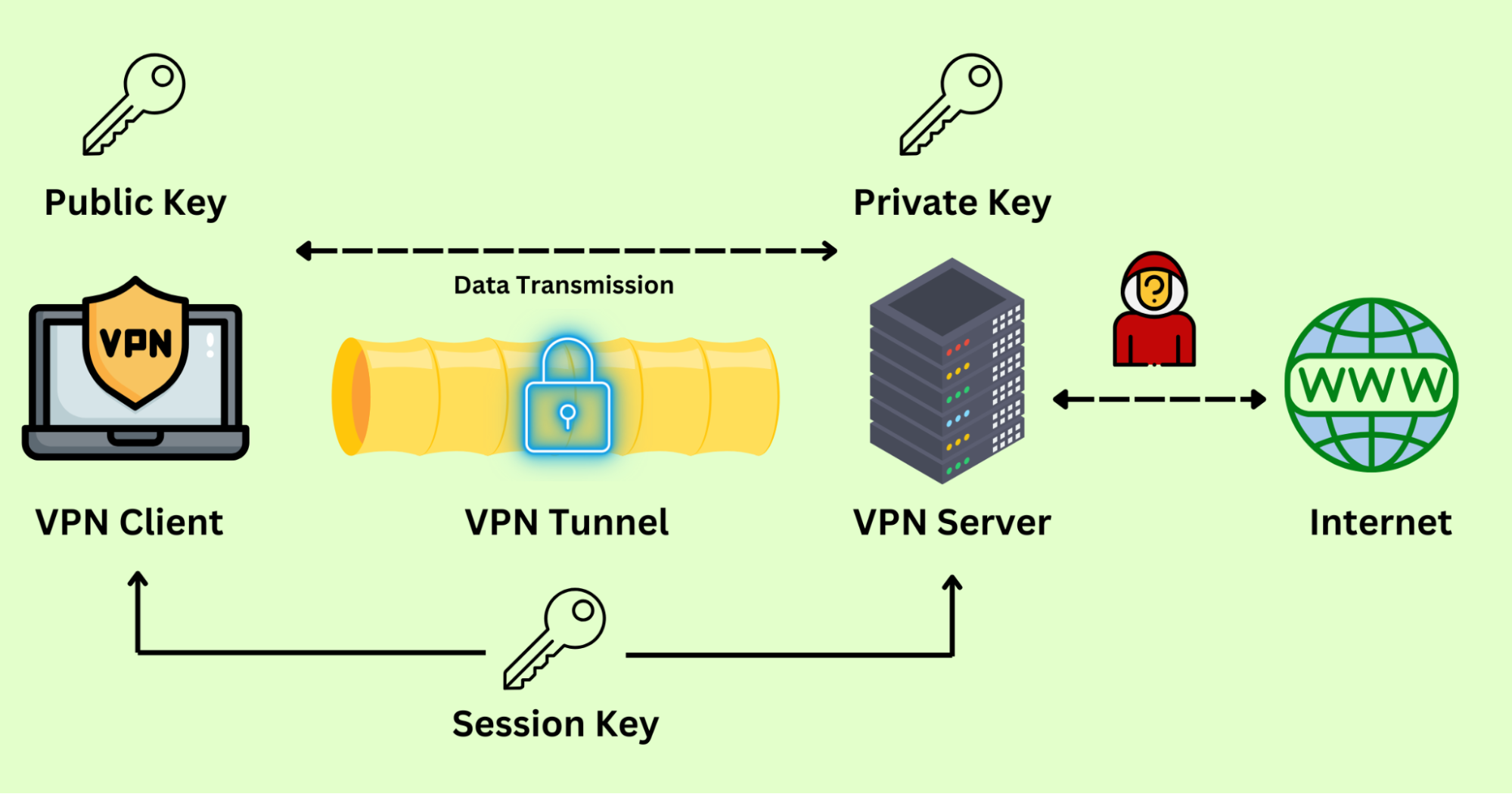
1. Asymmetric Key Exchange:
- First, the VPN client and the VPN server should do a handshake. The client sends a Hello message, informing the server of the encryption algorithms it supports.
- The VPN server responds to the hello, specifies the encryption algorithm to be used, and sends a message to the client containing its TLS certificate issued by a trusted certificate authority.
- The certificate sent to the client contains a public key for the Asymmetric Key Exchange.
- Upon receiving the certificate, the client verifies its authenticity with the certificate authority to ensure the server is legitimate and not a rogue hacker posing as an intermediary.
- After successful verification, the VPN client uses the public key to encrypt data(a symmetric key), which is then sent to the VPN server.
- Then the VPN server can decrypt the symmetric key with a private key corresponding to the public key.
2. Symmetric Encryption:
- The second phase will use symmetric encryption to generate a new, unique symmetric key known as the session key.
- Once the session key is established, the VPN client and VPN server function like two trusted parties sharing the same “secret code.” Throughout the entire VPN session, all data encryption and decryption rely on this unique key.
3. Data Transmission
- Next, the encrypted key will be sent to the VPN server with the encryption algorithm.
4. Integrity Check
- Finally, the server will use the integrity algorithm to verify that the encrypted data has not been tampered with and decrypt the symmetric key with the private key.
- Now, your data can be encrypted/decrypted by the VPN client and server with the symmetric key.
Step 4. Decrypt Data
The server decrypts the data to its original text and sends it to the intended website.
Step 5. Return Path
After the target website returns the data, the VPN server re-encrypts it and transmits it back to the user’s device through the VPN tunnel. Upon receiving the data, the client decrypts it using the corresponding key and then displays the webpage or application content to you.
The Benefits of VPN Encryption
At its core, VPN encryption is the very essence of a VPN. It directly determines whether your online protection is truly robust and trustworthy.
Enabling VPN encryption delivers significant advantages across these key areas:
- Security: Hackers can no longer spy on or intercept your network data. This not only effectively prevents data leaks but also shields you from common threats like scams, phishing, and DDoS attacks.
- Privacy Protection: With VPN encryption, third parties lose the ability to track your browsing activities. Whether it’s your ISP, online advertisers, or data analytics platforms, they cannot access your personal info.
- Anonymity Assurance: VPN encryption hides your real IP address and online footprint, allowing you to navigate the digital world invisibly. Think of it as your digital cloak of invisibility, making truly safe browsing possible.
- Lift Geo-Restrictions: Encrypted data helps you circumvent geo-blocks, granting seamless access to content from different regions. For instance, you can stream overseas Netflix libraries or get cheaper flights, enjoying both security and freedom.
Key Components of VPN Encryption
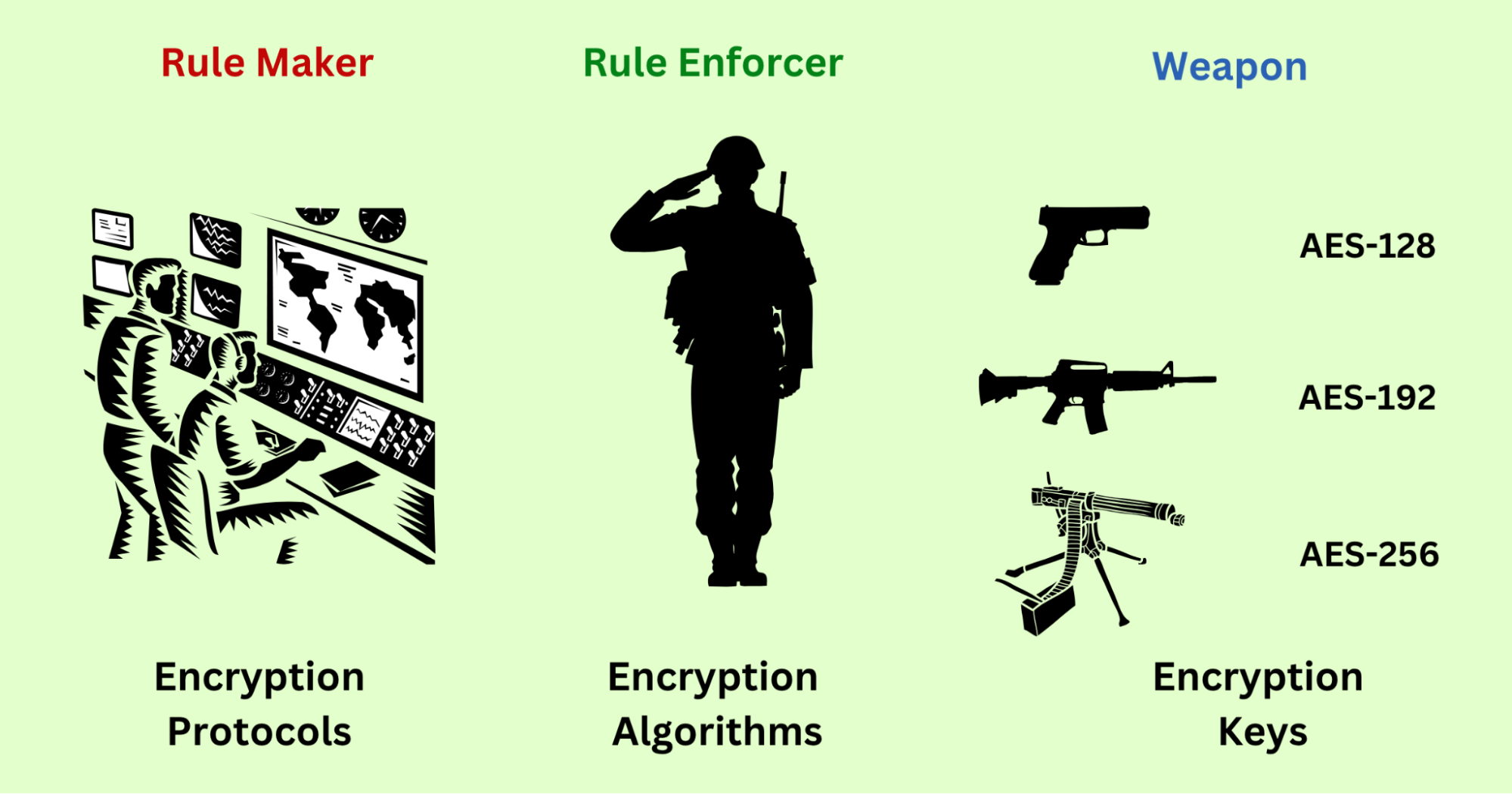
Within the entire VPN encryption system, three key components deserve special attention:
- Encryption Protocols – The Rule Maker: Define the rules and methods for data transmission.
- Encryption Algorithms – The Rule Enforcer: Perform the actual encryption/decryption according to the rule.
- Encryption Keys – The Enforcers’ Weapons: Provide the values for the algorithms to operate.
Encryption Protocols
Within a VPN encryption system, protocols function as the master orchestrating the entire process of data encryption and transmission. Different VPN protocols operate under distinct rules and mechanisms, resulting in varying levels of encryption strength and connection experiences.
Common VPN protocols are listed below:
- OpenVPN: A classic open-source protocol renowned for its high security and stability. As the “veteran” of the VPN world, it remains widely used today.
- WireGuard: A new-generation open-source protocol that has surged ahead with its minimalist design, blazing speeds, and robust security.
- L2TP/IPsec: Combines L2TP with IPsec, offering flexibility and configurability suitable for diverse scenarios.
- IKEv2/IPsec: Features exceptional reconnection speed, particularly ideal for mobile users, maintaining stability during network switches.
💡Extra Tip: Beyond these common protocols, many VPN providers develop proprietary encryption protocols to enhance performance, such as the Everest protocol of X-VPN.
- Everest: A private protocol integrating high speed, robust security, and exceptional unblocking capabilities, designed to deliver a smoother, more unrestricted online experience.
Protocol | Encryption Ability | Speed | Unblock Ability |
|---|---|---|---|
OpenVPN | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ |
WireGuard | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ |
L2TP/IPsec | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ |
IKEv2/IPsec | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ |
Everest | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ | ♥︎♥︎♥︎ |
Encryption Algorithms
Encryption algorithms are mathematical formulas used to convert plain text into unreadable, garbled text and vice versa. Its existence ensures that even if data is intercepted, unauthorized individuals cannot comprehend its contents.
Among numerous algorithms, the Advanced Encryption Standard, also called AES, stands as the most widely adopted and trusted representative, regarded as the industry gold standard for modern VPN encryption. With its exceptional security and efficient encryption performance, it has become the core technology for various secure communication systems worldwide.
Among its variants, AES-256, the most secure version, represents the pinnacle of security. It encrypts data into 256-bit blocks, making it virtually impossible for hackers to decrypt via brute-force attacks due to the required computational power. Consequently, top-tier VPN providers like X-VPN adopt AES-256 technology, delivering military-grade encryption protection to users.
💡Overview of Other Common Encryption Algorithms:
- ChaCha20: Renowned for high speed and robust security, it stands out as a star among next-generation encryption algorithms and is widely adopted in modern protocols like WireGuard.
- Blowfish: One of the early common encryption algorithms, but it has gradually been phased out due to multiple security vulnerabilities.
- 3DES: Evolved from the older DES algorithm, it offers improved security but remains less efficient and reliable than AES.
Different VPN protocols utilize different encryption algorithms, which means the combination of protocols and algorithms determines the security level and effectiveness of VPN encryption.
💡Key algorithms supported by mainstream VPN protocols:
- OpenVPN: AES (128-bit, 192-bit, 256-bit), Blowfish
- IPsec: AES (128-bit, 192-bit, 256-bit), 3DES, Blowfish
- L2TP/IPsec: AES (128-bit, 192-bit, 256-bit), 3DES
- IKEv2/IPsec: AES (128-bit, 192-bit, 256-bit), 3DES
- WireGuard: ChaCha20
Encryption Keys
In a VPN encryption system, a key is a random string of data that works in tandem with an algorithm to encrypt and decrypt online data.
Typically, the same encryption algorithm can support different key sizes. The longer the encryption key, the harder it is to crack, and the stronger the VPN encryption becomes. That’s why even the fastest computers on Earth would take billions of years to crack AES-256.
💡Such as:
- AES: Supports key sizes of 128, 192, and 256 bits.
- Blowfish: Supports variable key lengths from 32 to 448 bits.
During the VPN encryption process, two types of keys are typically involved:
- Symmetric keys
- Asymmetric keys
Each plays a great role in ensuring the security and integrity of VPN data transmission.
Types of VPN Encryption
Based on different key types, VPN Encryption using TLS protocol is also commonly categorized into Asymmetric Encryption and Symmetric Encryption.
Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric Encryption is commonly employed during the initial phase of establishing a VPN connection, often referred to as the “handshake phase.”
During the handshake process, Asymmetric Encryption generates a pair of public and private keys. The sender will encrypt the data using the public key, while the receiver will decrypt the ciphertext using the corresponding.
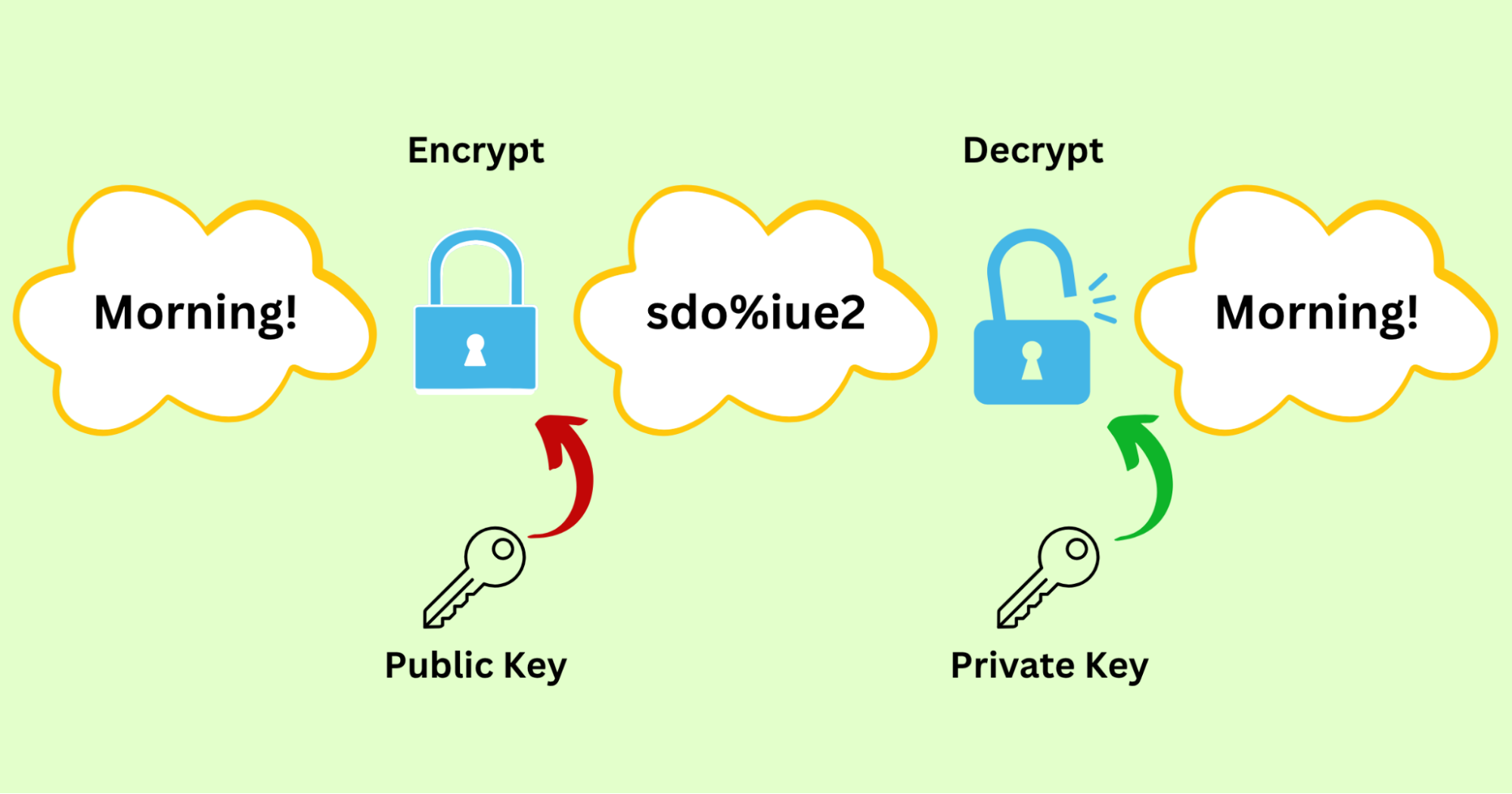
💡Check an example for you to understand this term clearly.
Scenario: Anna wants to send a private message to Juli.
Keys Generation:
- Juli creates a pair of keys.
- Public key: ju123
- Private key: cuteJuLi
Keys Distribution:
- Juli sends the public key to Anna and keeps the private key for herself.
Encryption:
- Anna creates a message to be sent: Morning!
- Anna encrypts the text with the public key Juli assigns to her.
- Morning! ➤ sdo%iue2
Data transfer:
- Anna uses the Internet to send the ciphertext to Juli.
Decryption:
- Juli uses her private key to convert the ciphertext into the original text.
- sdo%iue2 ➤ Morning!
Asymmetric Encryption uses two distinct keys—even if the public key is widely distributed, only the party holding the corresponding private key can decrypt the data. This is precisely why this encryption method offers exceptional security and reliability. In other words, even if hackers obtain the public key, they remain powerless to access the encrypted content.
However, robust security comes at a cost—Asymmetric Encryption requires more time to perform complex mathematical calculations, making it somewhat cumbersome when handling large volumes of VPN data transmission.
Thus, more efficient Symmetric Encryption took center stage.
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric Encryption relies on the same key relies on the same key to encrypt and decrypt data. This means the sender and receiver must share one key to ensure secure and seamless communication.
To illustrate, it’s like the secret telegrams exchanged between agents in old-school spy films. Only those who understand Morse code (the symmetric key) can correctly decipher each other’s messages.
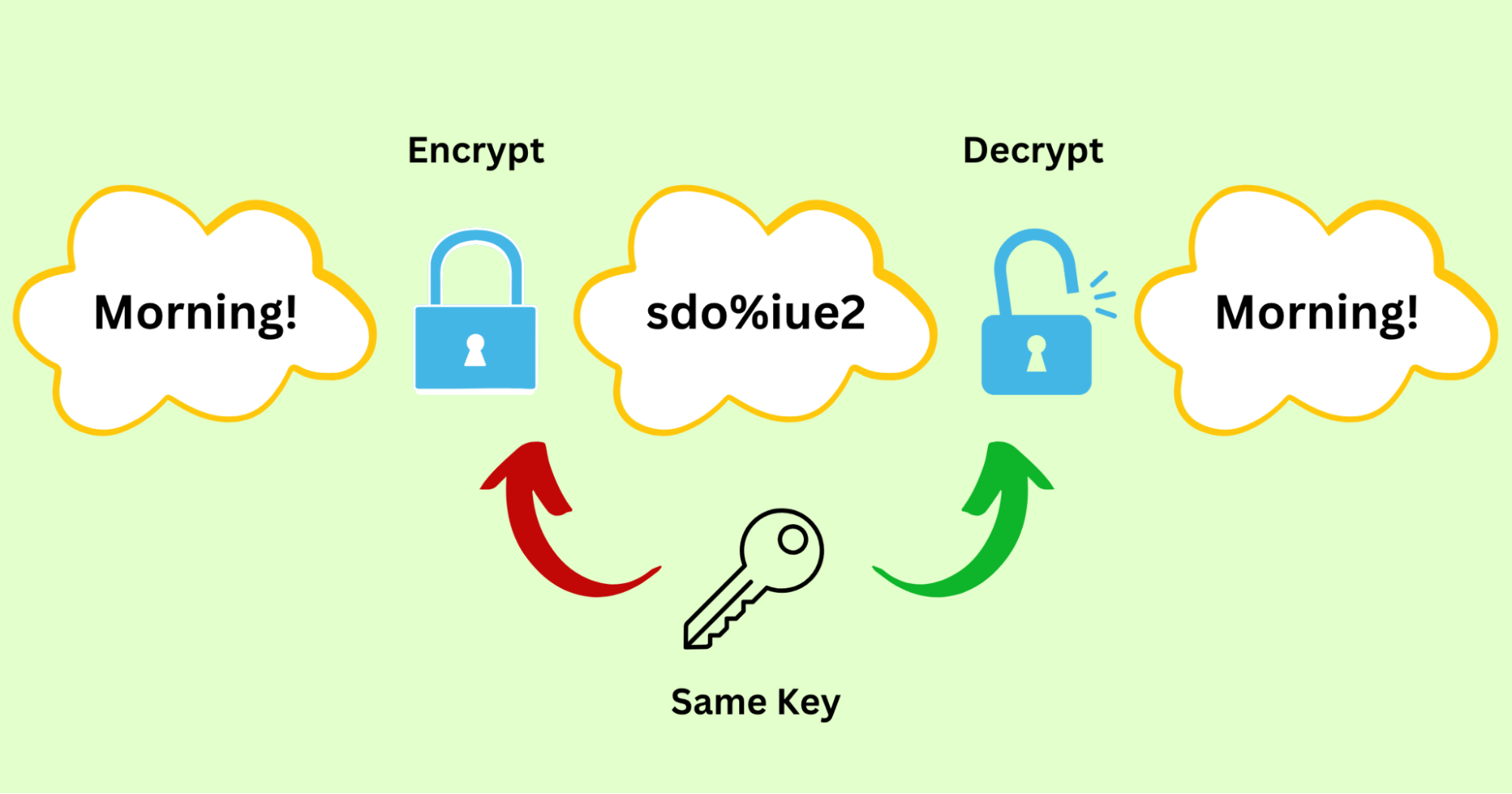
💡Here’s a vivid example.
Scenario: Anna sends the intelligence she got from spying to Juli
Keys Generation:
- They agreed in advance to use a codebook named AJ.
Encryption:
- Anna creates a message to be sent: Morning!
- Anna encrypts the text with the AJ code.
- Morning!➤ sdo%iue2
Data transfer:
- Anna sends the ciphertext to Juli.
Decryption:
- Juli converts the ciphertext into the intelligence with the AJ codebook.
- sdo%iue2 ➤ Morning!
Compared to Asymmetric Encryption, Symmetric Encryption involves lower computational complexity, faster processing speeds, and higher efficiency, making it highly suitable for encrypting massive amounts of data.
Therefore, within a VPN’s encryption framework, Asymmetric Encryption establishes secure connections, while Symmetric Encryption handles the actual VPN data transfer. Each plays its distinct role while working in close coordination—one lays the security foundation, the other ensures efficient operation, enabling VPNs to deliver unbreakable security protection while maintaining a smooth, stable connection experience.
Pro Tip: How to Test VPN Encryption?
Encryption is the absolute nucleus of VPN functionality, but as a normal user, you might wonder: Is my VPN really encrypting traffic? And how can I determine if a VPN’s encryption is robust enough?
No worries. We’ll show you how to test VPN encryption below using X-VPN, a reliable VPN that provides both a premium plan and a free plan. Just tap the button below to get a VPN download, and you can test VPN Encryption even without an account or cost!
・Standout Encyption Ability・Free Version・Rich Protocols Supports
Check the Encryption Protocol
First, you need to confirm the type of encryption protocol currently used by your VPN.
If your goal is to achieve the highest level of security protection, it is recommended to choose proven high-security protocols such as Everest, OpenVPN or WireGuard.
Leak Tests
The fundamental purpose of VPN encryption is to prevent data from being leaked or intercepted during transmission, ensuring your privacy remains uncompromised.
Therefore, the most direct way to verify encryption effectiveness is to check for risks such as DNS, IP, or WebRTC leaks while the VPN is active. If test results show no leaks, congratulations, your VPN encryption is indeed fulfilling its security responsibilities.
Check IP Leak
- Aim: Check if your real IP address is hidden.
- Tool: IPv6 Leak Test or ipleak.net.
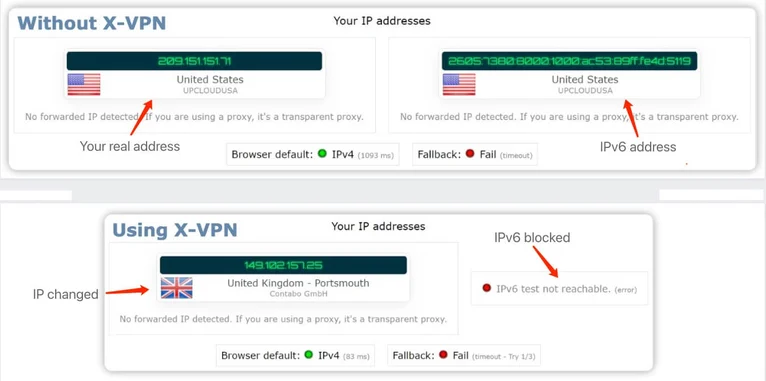
IPv6 Leak Test Results of Using X-VPN
Check DNS Leak
- Aim: Check for DNS leaks. If your DNS requests leak, your online footprints will be exposed, revealing the websites and services you visit.
- Tool: DNS Leak Test or dnsleaktest.com.
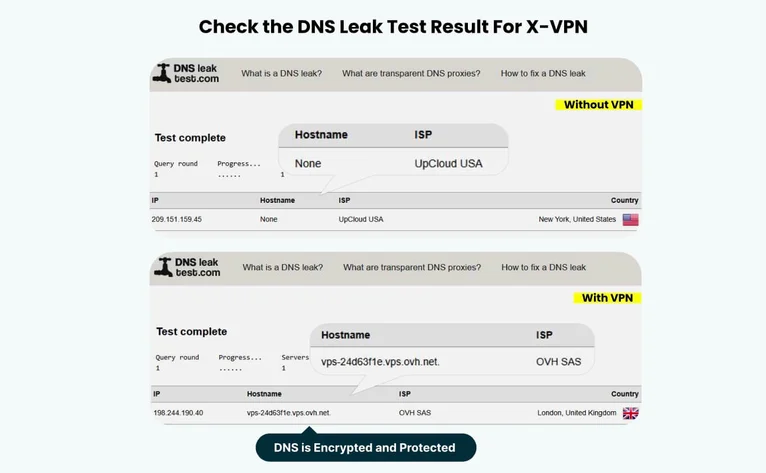
DNS Leak Test Results of Using X-VPN
Check WebRTC Leak
- Aim: Ensure your device’s browser does not reveal your real IP address through WebRTC leaks.
- Tool: WebRTC Leak Test or browserleaks.com.
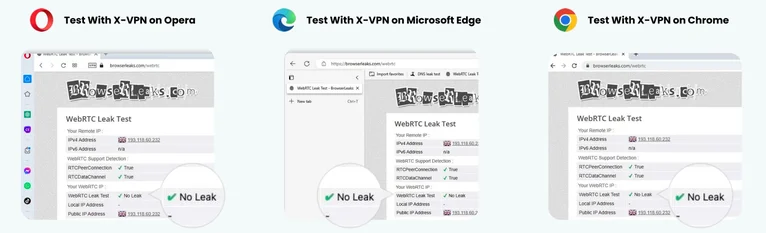
WebRTC Leak Test Results of Using X-VPN
Packet Sniffing
A packet sniffer can capture real-time network traffic and display detailed information about each data packet. If the data is unencrypted, it appears as clear, readable text; once VPN encryption takes effect, the packet contents become a jumble of random characters, completely unrecognizable.
Using the professional tool Wireshark, you can easily verify whether VPN encryption is truly active.
- Aim: Capture and analyze network data to check whether it is encrypted.
- Tool: Wireshark.
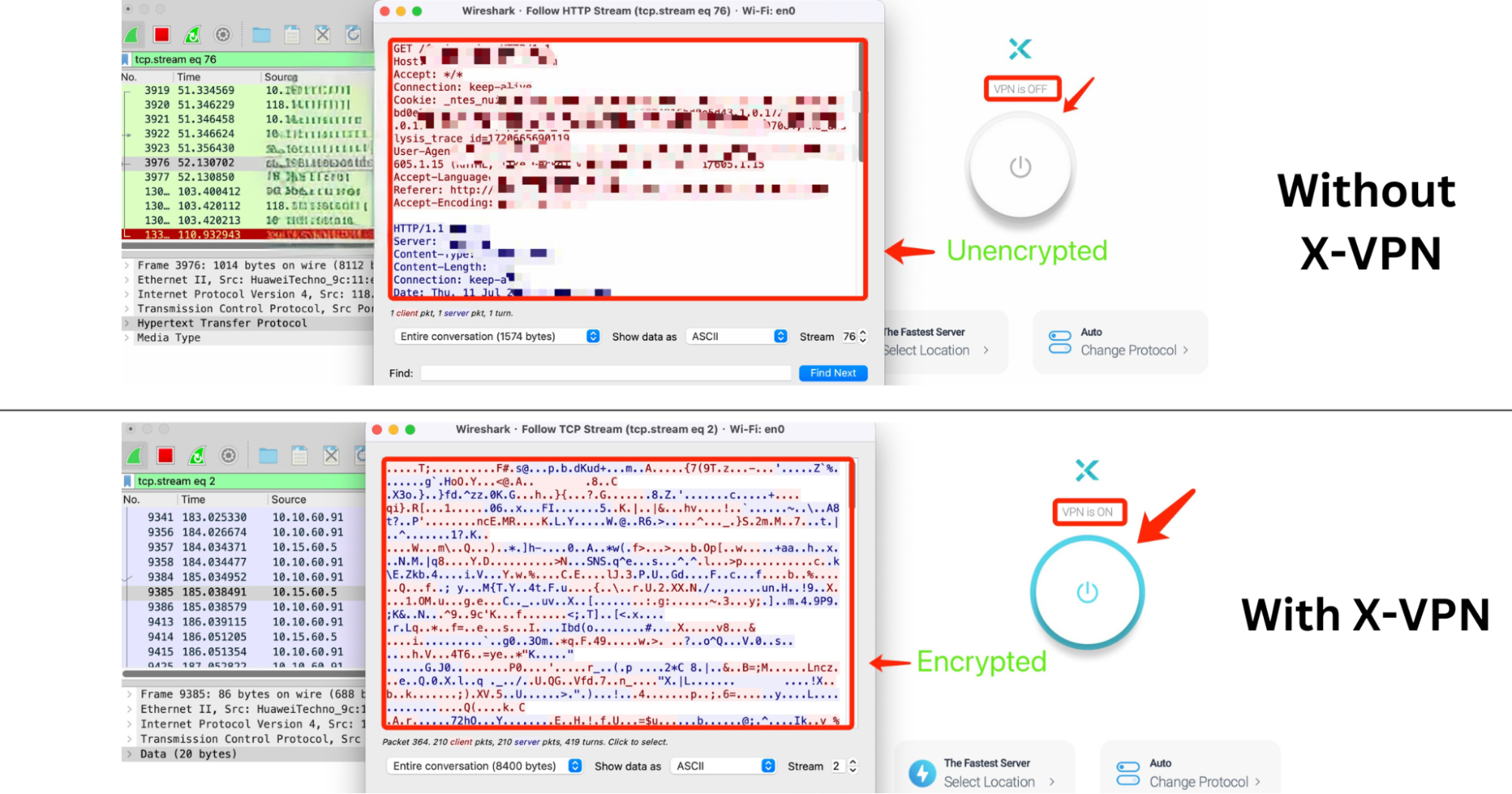
Packet Sniffing Results of Using X-VPN
By conducting a series of leak tests, now you can validate whether the VPN truly delivers on its promised security performance.
Conclusion
While the underlying mechanisms of VPN encryption are quite complex, using it couldn’t be simpler. After reading this article to grasp the fundamentals, download X-VPN and tap Connect—robust encryption protection and a full suite of seamless online security capabilities will be instantly activated.
FAQs
Does a VPN encrypt your IP?
Strictly speaking, a VPN does not directly encrypt your IP address. However, it replaces your real IP with the IP address of the VPN server you connect to, effectively concealing your identity and preventing others from tracing your network origin—a result that is nearly equivalent to encrypting your IP.
What is the strongest encryption for VPN?
Given that key length is directly proportional to security strength, AES-256 encryption is widely recognized as the strongest encryption for VPN. Renowned for its exceptional security and unbreakable nature, it is extensively adopted by governments, the military organizations, and various security agencies to safeguard confidential communications.
Do VPNs actually stop hackers?
Yes, VPNs do stop hackers. They build a robust online defense through powerful encryption, placing a “digital mask” over your identity so hackers cannot identify you or track your online activities.
Are VPN and Encryption the same?
A VPN is a protective tool designed to safeguard online security and privacy. Think of it like a police officer’s gear bag—complete with a bulletproof vest, helmet, handgun, handcuffs, and a stun gun. In the VPN world, these tools correspond to different functions: encryption, traffic tunneling, double VPN, kill switch, and more. Encryption is just one crucial component—like the handgun—important, but not the whole story.