While a VPN builds a secure tunnel to transmit your data, the VPN protocol determines how your data is transmitted over it. Different VPN protocols vary greatly in their speed, security, compatibility, stability, and undetectability.
This guide walks you through VPN protocols using simple words, aiming to help even VPN beginners choose the right protocol for different online activities.
Table of Contents
What Are VPN Protocols?
VPN protocols are the set of rules that govern every step of the secure connection between your device and a VPN server, from the initial handshake and encryption to the final transmission of your data.
Think of VPN as a secure delivery service. VPN Protocols are the procedures and rules that determine how your package is wrapped, what shipping methods it uses, etc. Different procedures will result in different speeds, privacy, and stability of delivery.
Categories of Protocols
However, just like the complex workings of a courier service, VPN protocols are also a partnership between different layers. There are standalone VPN protocols and also protocols that are used only for tunneling, encryption, or transmission. To avoid confusion in the following sections, we first divide the term “protocols” into 6 categories:
- Standalone VPN Protocols: Ready-to-use solutions that handle the entire connection process, including tunnel encapsulation, encryption, transmission, and so on. Such as WireGuard, OpenVPN and the proprietary protocols developed by some VPN service providers.
- VPN Tunneling Protocols: Specialized in creating the “tunnel” for data by encapsulating original packets. They typically provide no or weak encryption and thus must be combined with a separate encryption protocol to build a secure VPN. Such as PPTP and L2TP (which is commonly paired with IPsec).
- Encryption Protocols: Specialized in encrypting data, and are often integrated into standalone VPN protocols. Such as SSL/TLS.
- Combination VPN Protocols: Complete VPN protocol solutions that pair two specialized protocols. One creates the tunnel. The other provides strong encryption. Such as L2TP/IPsec and IKEv2/IPsec.
- Transport Layer Protocols: Specialized in ruling data transmission. All VPN protocols are built on top of these. Such as TCP, UDP.
- Proxy Protocols: Technologies that prioritize traffic obfuscation, not a true VPN protocol. Such as V2Ray/Xray, Shadowsocks.
Strictly speaking, only standalone VPN protocols, combination VPN protocols, and some VPN tunneling protocols, like PPTP, can be considered complete and true VPN protocols.
Common Types of VPN Protocols
Based on the above categories of protocols, the following are some common types of standalone VPN protocols. Other common protocols and technologies will be introduced in the next section.
1. PPTP
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) is a first-generation VPN protocol developed by Microsoft. It uses both TCP and GRE to encapsulate and transmit PPP packets. While simple to set up and fast due to its minimal encryption, it is now considered completely insecure due to multiple known vulnerabilities and is out of date.
| Release Date | 1995 |
| Category/Position | VPN Tunneling Protocol |
| Features | Fast speed, good compatibility, easy to set up |
| Cons | Highly insecure, easily blocked and hacked |
2. L2TP/IPsec
L2TP/IPsec (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol with IPsec) combines L2TP, which creates the tunnel, with IPsec, which handles encryption to offer strong security. It is the successor to PPTP, and is built into most modern operating systems.
| Release Date | 1999 |
| Category/Position | Combination VPN Protocols |
| Features | Good security, widely supported |
| Cons | Slow speed and may be blocked by firewalls |
3. OpenVPN
OpenVPN is an open-source, cross-platform, and currently the most commonly used VPN encryption protocol. OpenVPN can be further divided into two types: OpenVPN TCP and OpenVPN UDP. The former focuses more on network security, while the latter offers better connection speeds.
| Release Date | 2002 |
| Category/Position | Standalone VPN Protocol |
| Features | Highly secure & configurable, bypasses firewalls |
| Cons | Requires third-party software, complex setup |
4. IKEv2/IPsec
IKEv2/IPsec (Internet Key Exchange version 2) is a powerful protocol pair known for its speed and remarkable stability, and is a part of the IPsec protocol suite. It can quickly re-establish a connection if your internet drops or switches, making it a top choice for users on the go.
| Release Date | 2005 |
| Category/Position | Combination VPN Protocols |
| Features | Fast, stable, highly secure, easy to configure |
| Cons | Can be blocked by firewalls, closed source |
5. WireGuard
WireGuard is a relatively new open-source VPN protocol and is widely called the “future of VPN protocols.” Unlike other general-purpose VPN protocols that utilize complex encryption algorithms, WireGuard simply repurposes existing algorithms to achieve simpler yet still secure encryption. Originally available only on Linux, WireGuard is now available on Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, etc.
| Release Date | 2020 |
| Category/Position | Standalone VPN Protocol |
| Features | Extremely fast & efficient, easy to set up |
| Cons | Relatively new and still maturing |
6. Proprietary VPN Protocols
Proprietary VPN Protocols are custom-built solutions developed by VPN companies to offer a superior user experience. A typical example is X-VPN’s Everest Protocol, which is designed for faster speed and stronger obfuscation.
| Release Date | Varies by provider |
| Category/Position | Standalone VPN Protocol |
| Features | Optimized for speed & user experience |
| Cons | Closed-source |
Key Supporting Protocols & Related Technologies
In addition to core VPN protocols, supporting protocols and other technologies are vital to modern secure connections.
1. TCP/IP
TCP/IP(Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is the foundational protocol suite that determines how data is transmitted. IP finds the path to the destination, and TCP ensures the data arrives reliably on that path.
| Release Date | 1970s |
| Category/Position | Transport & Network Layer Protocol |
| Features | Reliable, error-checked, ordered data delivery |
| Cons | Higher latency, more overhead |
2. UDP
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is the other core transport protocol of the Internet, known for its raw speed. Unlike TCP, it sends data without establishing a connection first, which makes it much faster but does not guarantee delivery or correct order.
| Release Date | 1970s |
| Category/Position | Transport Layer Protocol |
| Features | Connectionless, low latency, minimal overhead |
| Cons | Unreliable, no ordering |
3. SSL/TLS
SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer / Transport Layer Security) is the cryptographic backbone that secures much of the internet, including HTTPS websites. It provides the essential “lock” for data that many standalone VPN protocols, like OpenVPN, rely on to build their secure tunnels.
| Release Date | 1995 |
| Category/Position | Encryption Protocol |
| Features | Ubiquitous, highly secure, enables HTTPS |
| Cons | Configuration-dependent, vulnerabilities if outdated |
4. QUIC
QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections) is a modern transport protocol that integrates TLS encryption directly on top of UDP. Its ability to reduce connection latency is being used by some VPN providers, like X-VPN, to build next-generation, faster proprietary protocols.
| Release Date | 2021 (HTTP/3 Standard) |
| Category/Position | Transport Layer Protocol |
| Features | Built-in encryption, reduced latency |
| Cons | Can be throttled |
5. Proxy Protocols
Instead of being a traditional VPN protocol, some proxies and technologies are often categorized as “Proxy Protocols” that prioritize traffic obfuscation. Typical examples are V2Ray/Xray and Shadowsocks.
| Release Date | 2019(V2Ray/Xray) |
| Category/Position | Proxy Protocols |
| Features | Strong obfuscation |
| Cons | Complex configuration |
VPN Protocols & Related Technologies Comparison
To help better master those common VPN protocols or proxy technologies, here’s a table briefly comparing their speed, security, stability, and obfuscation ability.
Protocols | Speed | Security | Stability | Obfuscation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
PPTP | ★★★★☆ | ★☆☆☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★☆☆☆☆ |
L2TP/IPsec | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★☆☆☆ |
OpenVPN | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ |
IKEv2/IPsec | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ |
WireGuard | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ |
Proprietary | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ |
V2Ray/Xray | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ |
Shadowsocks | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ |
1. All ratings are based on the latest, properly configured versions of the protocols.
2. Ratings for proprietary protocols are generalized estimates. Their actual performance, especially in security and obfuscation, varies by providers.
How to Choose? By Activity, By Protocol
So, now we basically know all the common types of VPN protocols, their features, drawbacks, etc. How to choose the right VPN protocol for your connection? By your activities.
The following recommendations focus on VPN protocols and advanced proxy tools. For transport layer protocols like TCP, UDP, and encryption protocols like SSL/TLS cannot be used alone to establish a VPN connection.
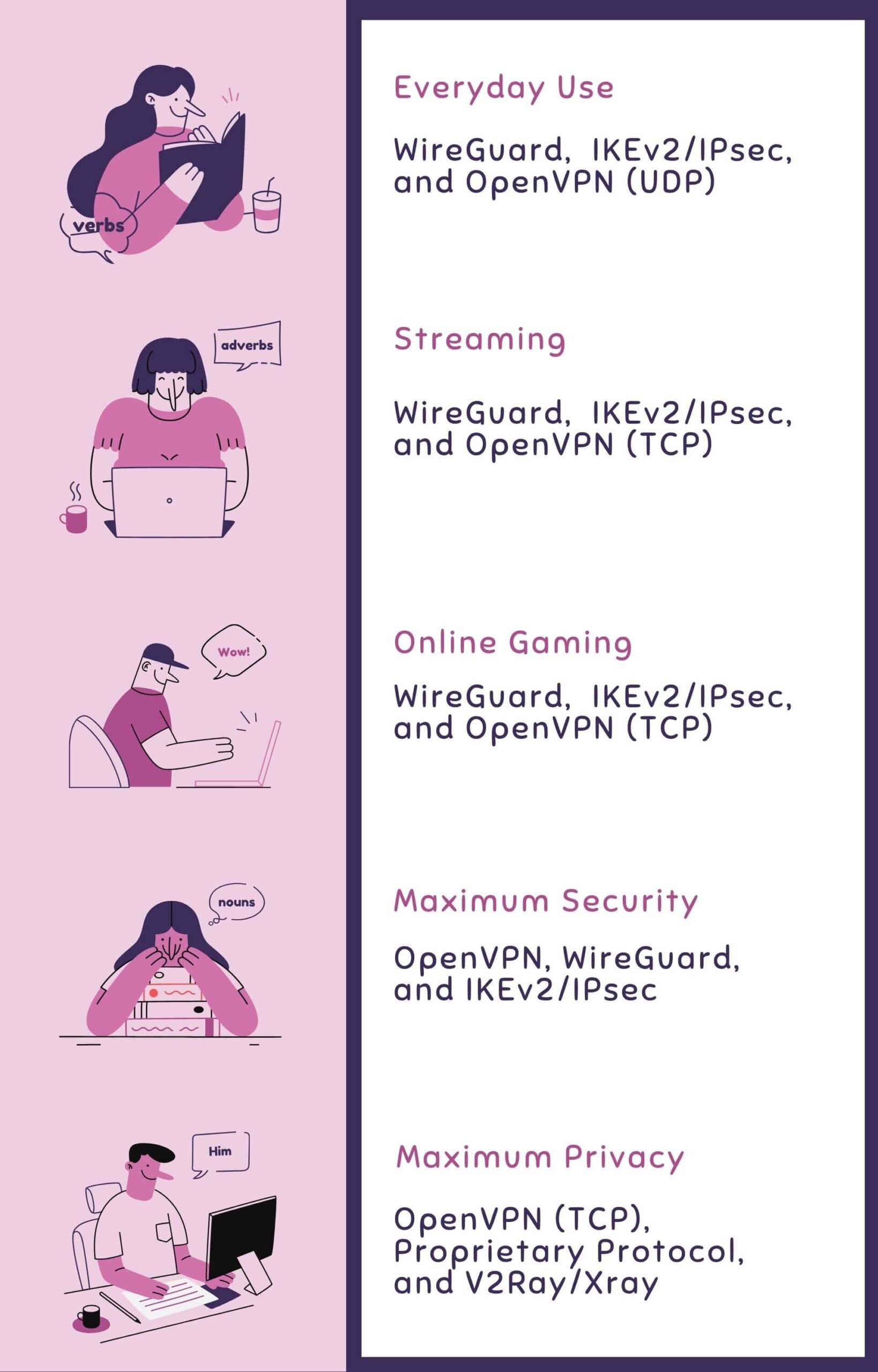
1. For Everyday Use
WireGuard, IKEv2/IPsec, and OpenVPN (UDP) are the top 3 recommendations for their balance between security, speed, and stability for web browsing, social media, and light downloads.
2. For Streaming & High-Bandwidth Activities
WireGuard, IKEv2/IPsec, and OpenVPN (TCP) stand out for their high speeds and minimal buffering, ensuring smooth HD video playback.
3. For Online Gaming & Low Latency
WireGuard, IKEv2/IPsec, and OpenVPN (TCP) suit online gaming and other activities that require low latency(ping) and a stable connection to avoid game lags and disconnections.
4. For Maximum Security & Sensitive Tasks
OpenVPN, WireGuard, and IKEv2/IPsec are ideal for tasks that need high security. They offer the highest level of privacy and encryption, suitable for handling confidential information.
5. For Maximum Privacy on Restricted Networks
OpenVPN (TCP), Proprietary Protocol(like Everest), and V2Ray/Xray are the top 3 recommendations for privacy on restricted networks. They can obfuscate and disguise your traffic, making it appear as normal data instead of VPN traffic.
Switching Between Protocols with X-VPN
Not all VPNs allow you to freely switch between VPN protocols depending on your activities. However, with X-VPN, you can enjoy the fastest speeds of WireGuard, the highest security of OpenVPN, and the robust obfuscation of our proprietary Everest protocol, which is built on the latest TLS, TCP, and UDP technologies, and even introduced the QUIC protocol for our mobile and TV users.
Support WireGuard & OpenVPN
Strong Proprietary Everest Protocol
Unlimited Free VPN
Smart Auto-Protocol Match
Conclusion
The technology behind VPN protocols might be complex, but using them for your digital life shouldn’t be. Pick up this handbook, and choose the right protocol according to your needs. Don’t forget to try the extensive protocol library of X-VPN and take control of your online privacy today.
FAQs
What’s the Best VPN Protocol?
There’s no single “best” VPN protocol. The ideal choice depends on your needs. WireGuard offers the best speed, and Proprietary Protocol guarantees obfuscation, while OpenVPN remains top-tier security.
What VPN Protocol Should I Use?
You should use a VPN protocol based on your online activities. Generally speaking, use WireGuard for streaming and gaming, and choose OpenVPN for sensitive tasks and privacy protection.
Can I Switch Between Different VPN Protocols?
Yes, you can easily switch between different VPN protocols with a VPN app. For example, with X-VPN, you can seamlessly switch between WireGuard for speed, OpenVPN for security, and our Proprietary Everest protocol for speed and obfuscation.
What Are the Fastest VPN Protocols?
WireGuard is consistently the fastest. Modern Proprietary protocols (like Everest) and IKEv2/IPsec are also excellent choices for speed.
What Are the Most Common VPN Protocols?
The most common and widely supported protocols are OpenVPN and IKEv2/IPsec. WireGuard is rapidly being adopted as a new standard due to its brilliant performance.
What Are the Most Secure VPN Protocols?
OpenVPN and WireGuard are considered the most secure. OpenVPN has a long, audited history, while WireGuard uses modern, foolproof cryptography.
What Are the Latest VPN Protocols?
WireGuard is the leading modern protocol. QUIC is also an emerging technology that some VPNs are using to build next-generation, faster services.